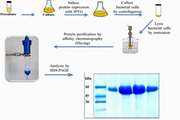
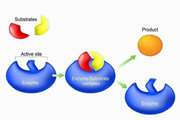
Development of an Electrochemical Nanobiosensor for Isolation and Detection of Cancerous Exosomes Containing PSMA and CD63 Antigens in Urine for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Cancer is a disease that results from the abnormal proliferation and growth of cells. It begins when mutations occur in the genes that regulate cell growth. Under normal circumstances, if a cell undergoes an irreparable mutation, it will undergo programmed cell death. However, if the cell is unable to undergo self-destruction, it and/or its progeny may divide uncontrollably with incorrect genetic information. Cancerous cells form tumors, which lead to multiple alterations in biochemical processes, gene expression patterns, and disrupt the balance between cell proliferation and death.
The computational and experimental study of the NLuc-NLRP3PYD protein, a dual-component luciferase biosensor, to enhance its efficiency in screening anti-inflammatory drugs
The inflammasome is a macromolecular complex of the innate immune system that, in response to a wide range of stimuli and pathogenic molecules, activates an inflammatory signaling cascade as a defense mechanism of the body. However, improper activity of the inflammasome can lead to autoinflammatory disorders and autoimmune diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders.
Design and Fabrication of Acoustic Wave Biosensor for the Detection of Cardiac TroponinI in Serum
In this study, the aim is to develop a high-sensitivity acoustic wave biosensor with a low detectable mass for the identification of cardiac troponin I. Love sensors, which are a type of surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensor, are designed in this research for the measurement of troponin I. A Love sensor consists of a transducer region and a sensor region.
Computational and experimental study on the structure and function of phenylalanine dehydrogenase in order to increase its efficiency as a diagnosis enzyme
Phenylalanine dehydrogenase (PheDh) is used in the diagnosis of phenylketonuria (PKU). In this condition, due to the inefficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase, there is a buildup of the amino acid phenylalanine in the body, which can lead to several issues, including intellectual disability. Therefore, early diagnosis of this disease in newborns is of great importance. For accurate disease diagnosis, the specificity of PheDh for phenylalanine, as well as the enzyme's stability, are crucial factors.
Study on the enzymatic production of 1,5 anhydroglucitol with QM/MM methods
The combination of 1 and 5 anhydroglucitol has been proposed as a marker for monitoring the blood sugar control status in diabetic patients. Measuring the levels of this compound in the serum of diabetic patients reflects blood sugar fluctuations over shorter periods compared to HbA1C. It can be used to assess postprandial blood sugar changes. Thus, this compound could serve as an indicator for the potential development of macrovascular complications, which may not be detectable through HbA1C testing alone.
Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Chiral Quantum Dots for Investigating Insulin Conductivity
Diabetes: A Common Endocrine Disorder Diabetes is the most common endocrine disease and is a clinical syndrome characterized by abnormal hyperglycemia resulting from insulin deficiency or resistance. Clinically, diabetes is one of the major risk factors for various complications, including nephropathy, retinopathy, neuropathy, and cardiovascular diseases. Due to various reasons, including the growing global population, the prevalence of obesity, and physical inactivity, the number of individuals with diabetes is steadily increasing.
Design of a Microfluidic Biosensor for the Isolation and Detection of Cancer Exosomes with EGFR Antigen
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) is a type of tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in various cancers and contributes to the growth of solid tumors. The physiological function of EGFR involves regulating epithelial tissue growth and homeostasis, and in certain cancers, it can act as a tumorigenic driver.
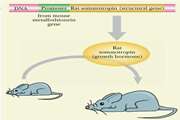
Investigation of the Effect of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone on Hepatic Alpha-Amylase Gene Expression in Mice
Food Safety and Health Food safety and health is a major concern for consumers. Today, artificial sweeteners are approved additives in food and beverages. One of these artificial sweeteners is Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone (NHDC), which has previously been studied in vitro for its effect as an activator of alpha-amylase enzyme.
Fabrication and Evaluation of Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogel Containing Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as Wound Dressing
Wound Dressing Selection A dressing is chosen based on the type, depth, location, and extent of the wound, as well as the level of exudate, infection, and adherence. Dressings are divided into two categories: traditional and modern. Traditional wound dressings (e.g., cotton and gauze) absorb a significant amount of moisture from the wound, which can severely dry out the wound surface, leading to reduced healing speed and pain during dressing removal.