The computational and experimental study of the NLuc-NLRP3PYD protein, a dual-component luciferase biosensor, to enhance its efficiency in screening anti-inflammatory drugs
The inflammasome is a macromolecular complex of the innate immune system that, in response to a wide range of stimuli and pathogenic molecules, activates an inflammatory signaling cascade as a defense mechanism of the body. However, improper activity of the inflammasome can lead to autoinflammatory disorders and autoimmune diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders.
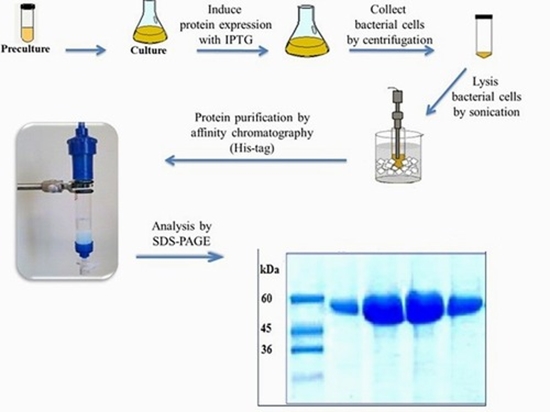
The inflammasome is a macromolecular complex of the innate immune system that, in response to a wide range of stimuli and pathogenic molecules, activates an inflammatory signaling cascade as a defense mechanism of the body. However, improper activity of the inflammasome can lead to autoinflammatory disorders and autoimmune diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders. Most common inflammasomes consist of three main components: a sensor domain, such as NLRP3 (with a pyrin domain, PYD), an adaptor protein like ASC, and an effector caspase such as caspase-1. Structural studies have shown that the cytosolic NLRP3 receptor undergoes oligomerization upon stimulation, ultimately driving the cell toward pyroptotic cell death. The split luciferase-based complementary assay is an advanced method for measuring protein-protein interactions during complex formation. This approach is based on the reconstitution of luciferase fragments, with each fragment (Nluc, Cluc) binding to one of the interacting proteins. The proximity of the luciferase fragments due to protein target interactions results in bioluminescence emission, which can be quantitatively measured by photon counting. In 2022, the use of the split luciferase complementation method for studying the interaction between components of the inflammatory complex and monitoring the NLRP3PYD-NLRP3PYD interaction was reported for the first time. In this study, in silico and in vitro techniques were employed to structurally engineer the NLuc-NLRP3PYD fragment of the aforementioned dual-component luciferase biosensor to improve performance. The dual-component luciferase complementation assay was utilized to monitor homotypic interactions, facilitating the use of this tool for screening inhibitors of NLRP3PYD self-oligomerization with anti-inflammatory activity.



comment