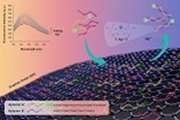
Preparation of N-doped carbon material derived from porous organic polymer as an active center to growth nickel cobalt phosphide for high-performance supercapacitors
In this study, nitrogen-doped porous carbon materials derived from Azo-bridged calix[4]resorcinarene porous organic polymer were synthesized via pyrolysis at various temperatures. Notably, this work represents the first successful fabrication of nitrogen-doped carbon materials utilizing the Azo group (N=N) as a nitrogen source.
Hemoglobin-Capped carbon dots synthesized via microwave green approach as a biosensor for specific cholesterol detection
This study explores the potential of hemoglobin-capped green-synthesized carbon dots (g-CD) as a biosensor for the specific detection of cholesterol. The CDs, synthesized using an environmentally friendly and convenient microwave green approach, derived from Wood Extract of Wild Cherry Shrub and utilizing hemoglobin as a capping agent, offer promising characteristics for cholesterol detection.
Phenylalanine as an effective stabilizer and aggregation inhibitor of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase
Aromatic compounds are known anti-amyloid aggregates. Their effect on amorphous aggregates of proteins is, however, less studied. We chose aromatic amino acids Trp, Tyr, and Phe, as well as another known stabilizer (i.e. Arg), as potential compatible solvents to be tested on Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase (BAA).
How biomimetic nanofibers advance the realm of cutaneous wound management: The state-of-the-art and future prospects
The results of a review article, co-authored by researchers from the Biosensor Research Center at the Endocrinology and Metabolism Research Institute of Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Azad University of Sciences and Research, Sharif University of Technology, the University of Barcelona, and the University of Central Florida, have been published in the prestigious journal Progress in Materials Science, which has an impact factor of 4.37 and a citation score of 5.67. This article reviews advancements and innovative methods in the design of biomimetic nanofibrous materials with high potential for wound healing and skin regeneration.
Mercury (II) sensing using a simple turn-on fluorescent graphene oxide based aptasensor in serum and water samples
Abstract A simple, highly sensitive, and selective fluorometric aptasensing platform based on aptamer and graphene oxide (GO) is proposed for the determination of mercury (II) ion (Hg2+). In the designed assay, two aptamer probes, a carboxy-fluorescein (FAM) labeled aptamer (aptamer A) and its complementary (aptamer B) with partial complement containing several mismatches and GO as the quencher were used.
Emergence of sweet ligand-protein complexes from seemingly non-sweet conformations
Sweet taste perception starts from the interaction of a sweet molecule with residues of the sweet taste receptor (STR). Yet, how the perception of sweet taste emerges from this interaction is still not clear. Here, we reveal a potential mechanism in the initial stages of this cascade
Electrochemical Sensing Based on Nanofibers Modified Electrodes for Application in Diagnostic, Food and Waste Water Samples
Electrochemical sensors and biosensors are today important analytical and monitoring tools in various fields, from agriculture and the food industry to environmental and biomedical/pharmaceutical applications.