Investigation of the Effect of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone on Hepatic Alpha-Amylase Gene Expression in Mice
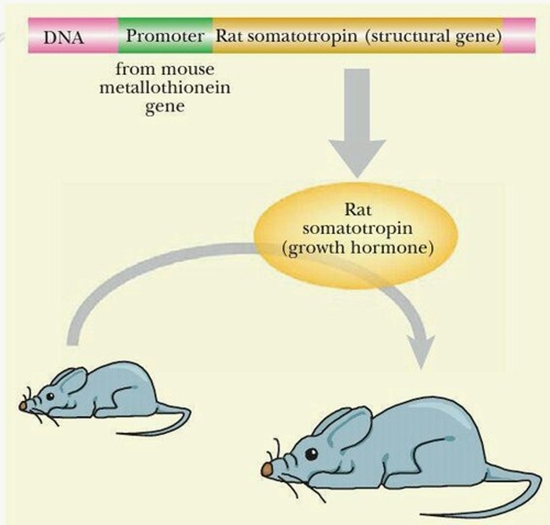
Food Safety and Health Food safety and health is a major concern for consumers. Today, artificial sweeteners are approved additives in food and beverages. One of these artificial sweeteners is Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone (NHDC), which has previously been studied in vitro for its effect as an activator of alpha-amylase enzyme.
Food Safety and Health
Food safety and health is a significant concern for consumers. Nowadays, artificial sweeteners are permitted additives in food and beverages. One of these artificial sweeteners is Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone (NHDC), which has previously been studied in vitro for its effect as an activator of the alpha-amylase enzyme. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of NHDC on the expression of the hepatic alpha-amylase gene in mice. Alpha-amylase catalyzes the glycosidic bond (α-1,4) in polysaccharides such as starch and glycogen. Sources of alpha-amylase include the salivary glands and pancreas, but studies have also shown that the liver serves as a source of alpha-amylase. Given that the liver plays a crucial role in carbohydrate metabolism, this study will focus on the expression of the alpha-amylase gene in the liver of mice.



comment