- 1403/11/14 The presence of the members of the Biosensor Research Center at the Gazing into the Future exhibition commemorating 170 years of experience and 90 years of excellence at Tehran University of Medical Sciences
- 1403/10/16 Development of an Electrochemical Nanobiosensor for Isolation and Detection of Cancerous Exosomes Containing PSMA and CD63 Antigens in Urine for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
- 1403/10/16 The computational and experimental study of the NLuc-NLRP3PYD protein, a dual-component luciferase biosensor, to enhance its efficiency in screening anti-inflammatory drugs
- 1403/10/12 Preparation of N-doped carbon material derived from porous organic polymer as an active center to growth nickel cobalt phosphide for high-performance supercapacitors
- 1403/10/12 Hemoglobin-Capped carbon dots synthesized via microwave green approach as a biosensor for specific cholesterol detection
- 1403/10/12 Phenylalanine as an effective stabilizer and aggregation inhibitor of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase
- 1403/10/09 Design and Fabrication of Acoustic Wave Biosensor for the Detection of Cardiac TroponinI in Serum
Biosensors at a Glance
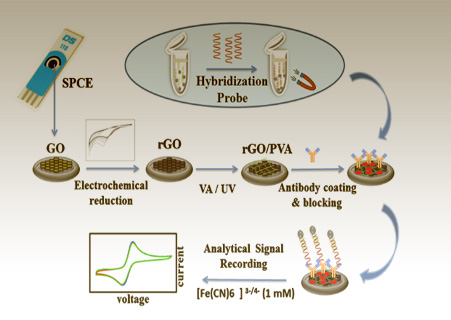
Biosensors are a group of measurement systems designed for the selective identification of analytes based on biological components and physical and chemical transducers. They can be classified according to the nature of the biological sensor and the mechanism of action of the transducer. In addition to conventional classification systems, terms like immunosensor and genosensor are often used to specify the diagnostic mechanism of a biosensor or the nature of the target molecule.
Biosensors consist of three components: a biological element, a detector, and a transducer. The design of biosensors has seen significant expansion in various fields of biology and medicine over the past two decades.
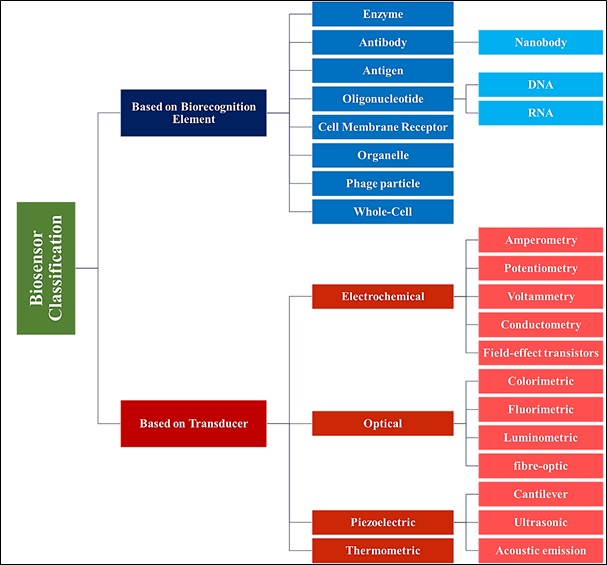
Biosensors can be categorized based on the nature of the biological sensor and the transducer's mechanism of action.
Furthermore, in addition to conventional classification systems, terms such as immunosensor and genosensor are often employed to define the diagnostic mechanism of a biosensor or the nature of the target molecule. An immunosensor is a biosensor that identifies a target molecule through the recognized interaction of antigen/antibody. A genosensor refers to a biosensor that uses specific and intelligent hybridization of nucleic acids as the main mechanism for target molecule identification. In genosensors, the target molecule is part of a known gene sequence or related sequences.
Point-of-Care Testing
In recent years, the application of biosensors in public health has been established. Regular measurement of analytes in biological samples is crucial for indicating the metabolic conditions of patients, especially those hospitalized or in intensive care units. Point-of-care testing (POC) systems are simple, sensitive, specific, and cost-effective, enabling the identification of biomarkers at home, in doctors' offices, at patients' bedsides, and even in workplaces. The design and development of such tests are essential for proper disease management and selecting appropriate treatments.
In many disorders, biomarker levels during the early stages of the disease are often below threshold concentrations, making their identification using conventional laboratory methods challenging. High-sensitivity POC tests facilitate the early detection of diseases and the assessment of disease recurrence after treatment.