Development and synthesis of DNA-based label-free electrochemical biosensor for detection of Enterocytozoon bieneusi using screen-printed gold electrode
Microsporidia are a large group of obligate intracellular parasites. In this study, a label-free electrochemical genosensor was developed to detect Enterocytozoon bieneusi using specific probe and electrode substrate, Mxene-Ti3C2/AuNPs/PDA. A 5' thiol-modified DNA probe, targeting 16S like ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene of E. bieneusi, was designed. The Ti3C2-AuNPs-PDA nanocomposite was synthesized.
Dead-End protein expression, function, and mutation in cancer: a systematic review
Cancer incidence is rising globally, particularly in aging populations. Understanding the genetic, cellular, and molecular mechanisms underlying cancer is crucial for developing effective interventions. Dead-end protein 1 (DND1), an RNA-binding protein, plays a pivotal role in germ cell regulation and tumorigenesis.
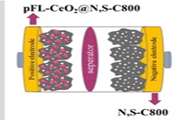
High-Performance Hybrid Supercapacitor Based on Morphology-Controlled Cerium Oxide on N,S-Doped Porous Carbon
In this study, we developed composite materials based on porous carbon doped with nitrogen and sulfur heteroatoms and integrated with ceria, targeting applications in high-performance supercapacitors.
Introducing rebaudioside A as a novel enzyme stabilizer: comparison with lysine on Aspergillus oryzae alpha-amylase inactivation and amorphous aggregation
BACKGROUND The role of amino acids and glycosidic compounds was investigated as edible and potential compatible stabilizing additives against Aspergillus oryzae alpha-amylase (AOA) inactivation and amorphous aggregation.
Wearable microfluidic immunosensors for point-of-care detection of bio-analytes: a critical review
Early and timely disease diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improved clinical outcomes. Antibodies and their fragments are among the most widely used affinity reagents in point-of-care (POC) assays because of their target specificity and affinity.
The Role of Nanomaterials in the Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Biosensors for Diabetes Management
The increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus necessitates the development of advanced glucose-monitoring systems that are non-invasive, reliable, and capable of real-time analysis. Wearable electrochemical biosensors have emerged as promising tools for continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), particularly through sweat-based platforms.
Advances in microfluidic technologies for antibody separation and detection: toward enhanced diagnostics and therapeutic applications
The rapidly advancing field of microfluidics has significantly transformed diagnostics and pharmaceutical industries by enabling precise control and analysis of fluids at the microscale.
Preparation of N-doped carbon material derived from porous organic polymer as an active center to growth nickel cobalt phosphide for high-performance supercapacitors
In this study, nitrogen-doped porous carbon materials derived from Azo-bridged calix[4]resorcinarene porous organic polymer were synthesized via pyrolysis at various temperatures. Notably, this work represents the first successful fabrication of nitrogen-doped carbon materials utilizing the Azo group (N=N) as a nitrogen source.
Hemoglobin-Capped carbon dots synthesized via microwave green approach as a biosensor for specific cholesterol detection
This study explores the potential of hemoglobin-capped green-synthesized carbon dots (g-CD) as a biosensor for the specific detection of cholesterol. The CDs, synthesized using an environmentally friendly and convenient microwave green approach, derived from Wood Extract of Wild Cherry Shrub and utilizing hemoglobin as a capping agent, offer promising characteristics for cholesterol detection.
Phenylalanine as an effective stabilizer and aggregation inhibitor of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase
Aromatic compounds are known anti-amyloid aggregates. Their effect on amorphous aggregates of proteins is, however, less studied. We chose aromatic amino acids Trp, Tyr, and Phe, as well as another known stabilizer (i.e. Arg), as potential compatible solvents to be tested on Bacillus amyloliquefaciens alpha-amylase (BAA).